Melanoma is one of the most dangerous skin cancers that develops from melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin – the pigment responsible for skin color. Early detection of melanoma is crucial for effective treatment and increases the chances of a complete cure. That’s why it’s so important to know the symptoms of melanoma and to examine your skin regularly.
Risk factors for melanoma
There are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing melanoma. These include:
- UV exposure: Excessive tanning, both in the sun and in tanning beds, is a major risk factor for melanoma. UV radiation damages the DNA of skin cells, which can lead to the development of cancer.
- Light complexion: People with light complexion, blond or red hair and blue or green eyes are more susceptible to melanoma. Their skin produces less melanin, which means they are less protected from the harmful effects of UV radiation.
- Large number of nevi: People with a large number of nevi, especially atypical ones, are at higher risk of developing melanoma.
- The occurrence of melanoma in the family: Melanoma can have a genetic basis. If there is a family history of melanoma, the risk of developing the disease is higher.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as after organ transplants or those with AIDS, are more susceptible to developing melanoma.
- Age: The risk of melanoma increases with age. People over the age of 50 are most likely to get the disease.
Symptoms of melanoma
Melanoma can appear anywhere on the body, but it most often develops on skin exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, back, chest and arms. It can also occur on the scalp, hands, feet and under the fingernails.
The symptoms of melanoma can vary, but the most common are changes in existing nevi or the appearance of new suspicious skin lesions.
The most common symptoms of melanoma include:
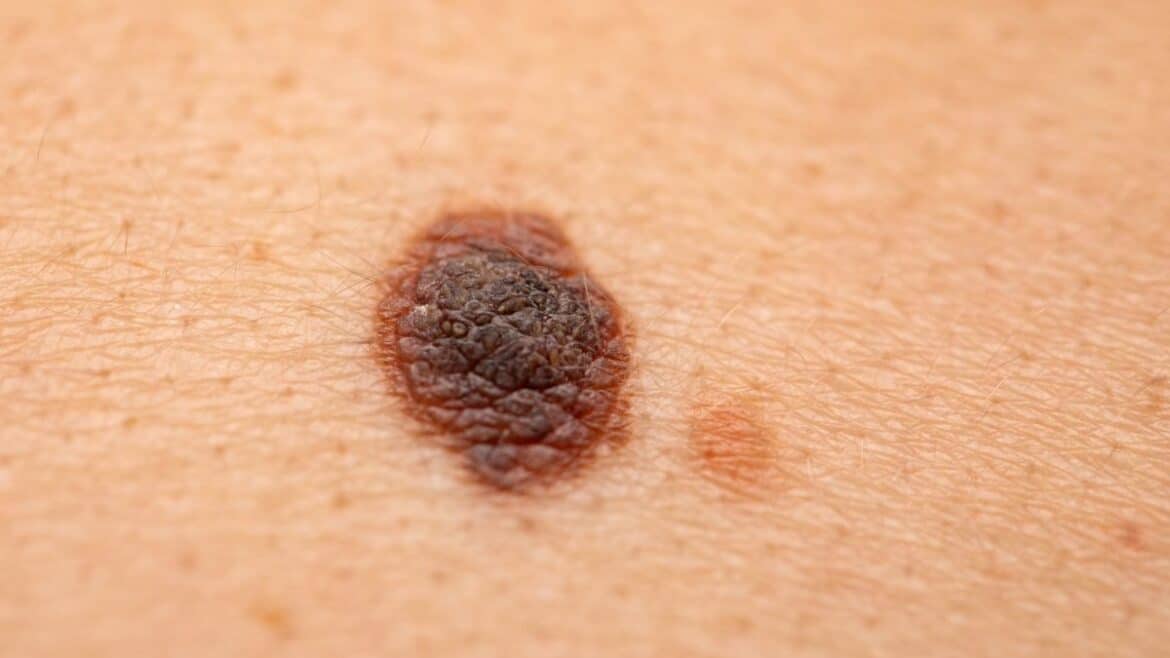
- Asymmetry: Melanoma nevi are usually asymmetrical, i.e. one half of the nevus is not a mirror image of the other half.
- Irregular edges: The edges of melanoma nevi are often irregular, jagged or obliterated.
- Heterogeneous color: Melanoma nevi can have different colors, such as black, brown, red, blue, white or gray.
- Large size: melanoma nevi are usually larger than 6 mm in diameter.
- Evolution: melanoma nevi change over time, such as growing, changing color, shape or texture. They may also itch, bleed or hurt.
Remember that not every skin lesion that meets the above criteria is melanoma. Many skin lesions are benign, but any suspicious lesion should be consulted with a dermatologist.
Melanoma diagnosis
If melanoma is suspected, the dermatologist will perform a dermatoscopic examination, which involves viewing the nevus under magnification using a dermatoscope. A dermatoscope is a special optical device that allows an accurate assessment of the structure of a nevus.
If the dermatoscopic examination raises suspicion of melanoma, the doctor will perform a biopsy of the nevus. The biopsy involves taking a section of the nevus for histopathological examination. Histopathological examination allows a definitive diagnosis of melanoma.
Melanoma treatment
Treatment of melanoma depends on the stage of the disease. Early stage melanoma can be treated surgically, by excising the lesion with a margin of healthy tissue. In more advanced stages, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are also used.
Melanoma prevention
The most important part of melanoma prevention is protection from UV radiation. Avoid excessive sunbathing, use high-factor UV filter creams, wear headgear and sunglasses.
Regular skin self-examination is also important. You should carefully examine your skin every month, noting any new or changing moles. If you notice any worrisome changes, consult a dermatologist.
Summary
Melanoma is a dangerous skin cancer, but early detection gives a good chance of a cure. That’s why it’s so important to know the symptoms of melanoma, regularly examine your skin and protect yourself from UV radiation. If you notice any worrying changes, consult a dermatologist.
Note:
The above article is for informational purposes and is not a substitute for visiting a doctor. If you have any doubts about your health, consult a specialist.